Agile Fundamentals Overview
Agile Glossary
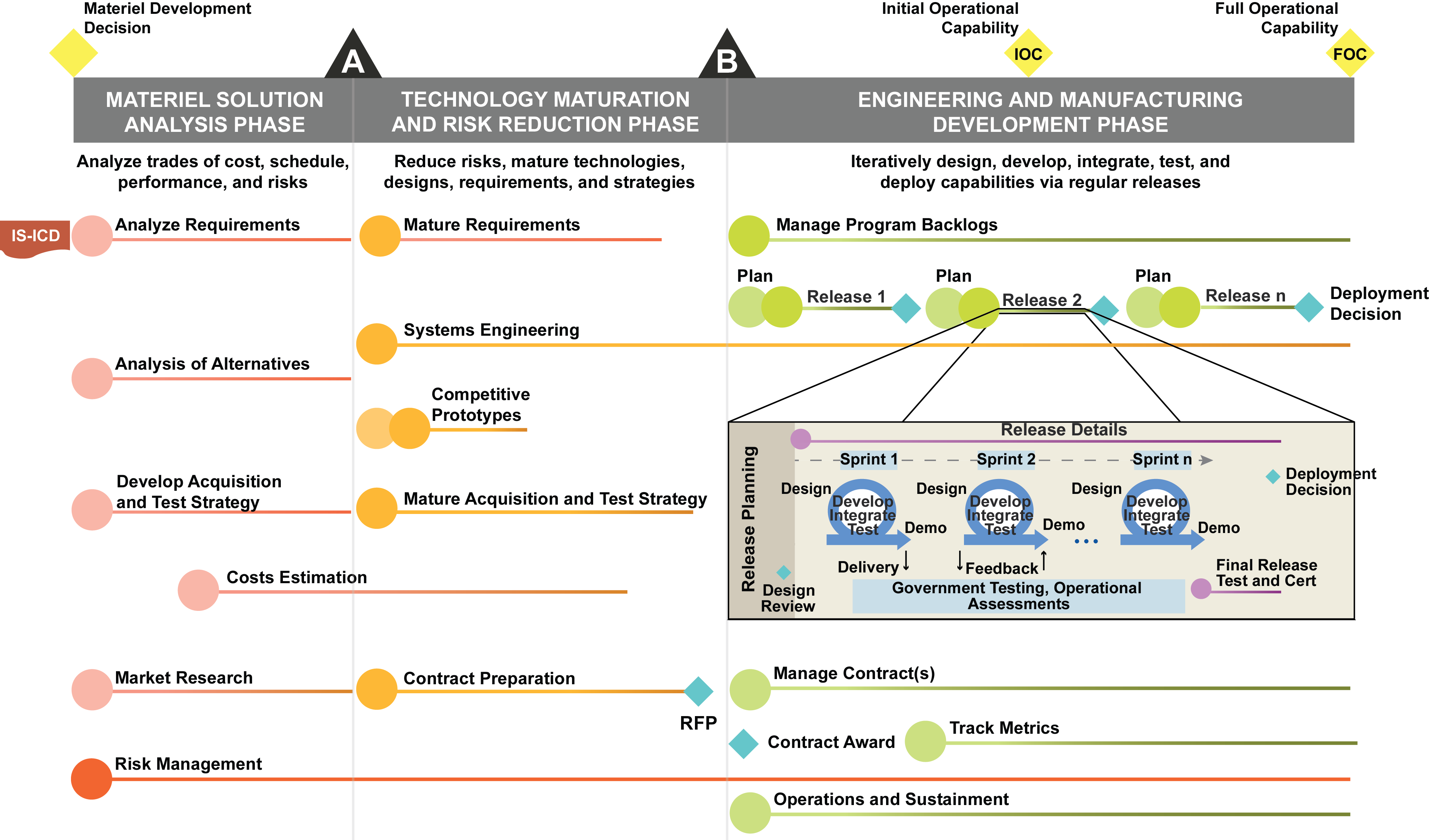
MATERIEL SOLUTION ANALYSIS (MSA) PHASE
Materiel Development Decision (MDD)
Analyze Requirements
Analysis of Alternatives (AoA)
Develop Acquisition Strategy
Market Research
Cost Estimation
Risk Management
TECHNOLOGY MATURITY AND RISK REDUCTION (TMRR) PHASE
Milestone A
Mature Requirements
Competitive Prototyping
Systems Engineering
Mature Acquisition Strategy
Contract Preparation
Risk Management
Request for Proposal
ENGINEERING & MANUFACTURING DEVELOPMENT (EMD) PHASE
Milestone B
Manage Program Backlogs
Release Execution
Manage Contracts
Metrics
Scaling Agile
Agile Fundamentals Overview
Agile is a set of software development principles that emerged in 2001 after 17 industry leaders created the Agile Manifesto to design and share better ways to develop software. Agile is the leading software development methodology in the commercial world with growing adoption across the government.
What is Agile?
Four primary characteristics should guide Agile adoption in Government:
- Structuring programs and processes around small, frequent capability releases
- Valuing working software over comprehensive documentation
- Responding to changes in operations, technology, and budgets during development
- Active user involvement throughout development to ensure high operational value
The foundation of Agile is a culture of small, dynamic, empowered teams actively collaborating with stakeholders throughout product development. Agile development requires team members to follow disciplined processes that require training, guidance, and openness to change. While Agile does impose rigor, the method does not consist of simply following a set of prescribed processes, but instead allows dynamic, tailored, and rapidly evolving approaches that suit each organization’s IT environment. Various Agile methods (e.g., Scrum, Extreme Programming (XP), Kanban, Test Driven Development (TDD), Disciplined Agile Delivery) have emerged, each with unique processes, terms, and techniques. These methods focus on the development team and associated stakeholders. Agile acquisition extends Agile development practices beyond the contractor development team to the government acquirer, users, and other stakeholders. It requires that both agencies and contractors change many acquisition roles, processes, and culture, thereby fostering a close government-industry partnership. This, in turn, demands investments in time, training, and continuous improvement to pay long-term dividends.
Why Agile?
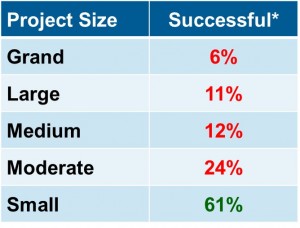
In the federal government, the acquisition of complex government-oriented IT systems are high risk, plagued with cost and schedule overruns, and often do not deliver capabilities to meet user requirements. Federal agencies struggle to deliver new IT capabilities to retire aging legacy systems. Given the pace of change in operations, technologies, threats, and budgets, agencies require an environment where capabilities can be iteratively delivered and responsive to changing priorities. The defense acquisition system for example was designed for large weapon systems that can take a decade or longer to define requirements, analyze alternatives, select a vendor(s), design, develop, test, produce, and deploy. IT generally operates in a more rapid environment than hardware systems where the state-of-art doubles every 18-months according to Moore’s Law. Countless studies including leading research from the Standish Group has demonstrated that smaller programs succeed in delivering required capabilities on cost/schedule at much higher rates than larger programs. Smaller programs are much lower risk to execute as they are easier to scope, estimate, design, develop, and test. They require less time during each phase, minimizing the opportunities for disruption. Smaller programs enable faster learning and smaller investments allowing for subsequent efforts to incrementally deliver capabilities that delight users.
Benefits of Agile
| Faster deliveries | Capabilities are regularly delivered in months, not the 5-10 years it takes for many large IT programs today to deliver via a waterfall methodology. |
| Responsive to change | Agile enables the program to react to changes in operations, technologies, budgets, threats, and other factors via small frequent releases. |
| Higher user satisfaction | Each release and sprint focuses on the highest priority requirements as determined by the user, providing users with frequent and consistent capability deliveries that address their needs. |
| Improved quality software | Daily and automated integration testing, small scoped releases, and routine demonstrations identify and address defects earlier in the development process with less rework. |
| Increased visibility into progress | Users, oversight authorities, and other stakeholders see regular progress in actual working software vice theoretical paper-based accounting estimates. |
| Reduced risk | Smaller scoped efforts are easier to design, plan, estimate, and execute and more resilent to changes. Additionally, smaller scoped projects have a lower “sunk cost” if they fail fast, fail early. |
| Improved productivity | In Agile more energy is focused on iteratively developing capabilities than planning and reporting documentation. |
Programs Well-Suited for Agile
While both practical experience and research findings strongly indicate the value of Agile for many IT acquisition programs, this approach is not appropriate in all cases. Programs well suited for Agile adoption include those that are:
| Software Intensive |
|
| Accessible Stakeholders |
|
| Uncertain Solution Space |
|
| Follow-on Increments |
|
See also How to Determine Projects Fit for Agile, GSA Tech Guide
Traditional vs Agile Programs
| Traditional | Agile | |
| Mindset | Define rigid requirements, design, develop, produce | Collaborative culture to iteratively deliver priority capabilities to users |
| Size/Scope | 5-Year Increments | <6 month releases |
| Requirements | Defined upfront via large CDDs and contracts | Iteratively defined and prioritized via dynamic backlogs |
| Contracts | Rigid, product based, long timelines, limited changes | SW Development-as-a-Service via iterative task orders |
| Cost Estimate | Exhaustive upfront analysis, rigid baselines | Iterative, integrated, collaborative |
| Testing | Long timelines following system development | Automated, daily, integrated throughout development |
Agile Barriers and Enablers in the Federal Acquisition Environment
Despite the success that Agile development has achieved in the private sector, commercial implementation of Agile does not directly translate to Agile adoption in the federal sector. The barriers to program structure, requirements, and contracting often stem from these key differences. The government must adhere to a set of rigorous policies, statutes, and regulations that do not apply to the same degree in the commercial sector. Following the rules that govern federal acquisition often involves a bureaucratic, laborious, and slow process that greatly influences how effectively Federal Agencies can implement Agile. The commercial sector has a different stakeholder management process than the government. Private firms are accountable to an internal and layered management structure that usually goes no higher than a corporate board of directors; the few possible external stakeholders (e.g., labor unions) rarely cause frequent and major disruptions. The government bureaucracy has layers upon layers of stakeholders with a high degree of influence that can create frequent and significant disruptions. Everything from a change in the political administration to budget sequestration can exert significant external influence on a program. The bureaucratic layers of government make it difficult to empower Agile teams to the same extent as in the private sector. The commercial sector has considerable latitude to make adjustments throughout the course of the development because companies closely link accountability, authority, and responsibilities to push decision making to the lowest levels. The government’s tiered management chain of command makes it difficult for the Agile team to be empowered to make timely decisions.
| Barriers | Enablers | |
| Acquisition Processes |
|
|
| Culture |
|
|
| User Involvement |
|
|
| Program Structure |
|
|
| Coordination |
|
|
| Experience and Training |
|
|
These enablers align with the recommended set of principles in the GAO report Effective Practices and Federal Challenges in Applying Agile Methods. They center on the Agile Manifesto themes of small, frequent capability releases, a dynamic requirements process that allows for the continuous prioritization of requirements, active involvement from the user community throughout the development process, and commitment to delivering working software based on a time-boxed schedule. Some efforts may succeed in implementing only a subset of these themes and delivering effective software solutions; however, one could argue that this would not constitute a pure Agile development.
Agencies could benefit from defining and standardizing Agile-based practices to ensure an agency-wide common understanding of what constitutes an Agile-based program or project.
Today, many efforts are inaccurately labeled as Agile, leading to misunderstanding and misrepresentation of Agile principles. After defining the principles, agencies needs to provide detailed guidance to the acquisition community that describes how to execute the Agile acquisition processes within their acquisition regulations and laws.
Embracing the Agile Culture
Agile practices, processes, and culture often run counter to those in the long-established defense acquisition enterprise. The Agile model represents a change in the way agencies conducts business. Programs must rethink how they are staffed, organized, and managed, as well as whether the business processes, governance reviews, and funding models that support an acquisition are structured to support Agile. To succeed, the Agile model depends on strong commitments at all levels of the acquisition process. Agile requires dedicated government involvement throughout the entire process in order to plan and integrate multiple releases, oversee development cycles, manage evolving requirements, facilitate collaboration, and obtain committed, active, and consistent user engagement. The government must establish a strong team to manage and complement the Agile development contractor. The optimal structure to foster a collaborative environment features physical co-location of the acquisition support team, which consists of the program staff, contractor, and supporting functional areas. In cases where close physical proximity of the team is not practical or feasible, programs can use collaboration tools for daily meetings, pair-programming, and frequent discussions with stakeholders.
One Air Force major IT program has the program office, contractor and end-users all located within a 7-mile radius. This close physical proximity has enabled the program’s adoption of an integrated Agile approach.
A culture of trust that spans the decision authority, developers, testing organization, acquirers, program management, and users is critical to Agile delivery. Close, dedicated Agile acquisition teams facilitate this model, but it must be further reinforced at the top. Leadership can signal that trust by empowering team members with decision-making authority based on clearly communicating a high-level strategy, requirements, and vision for the acquisition. An analogy to the military term “Commander’s Intent” can clarify this concept. Commander’s Intent is a concise expression of the purpose of an operation – a description of the desired end state and the way that goal facilitates transition to future operations. It allows adaptation, so that a mission can continue even when the operation does not go as planned. For Agile, the overall plan represents the intent. If the plan does not work as expected, the team alters the plan while continuing to focus on the intent. This requires the team to build relationships that promote trust, collaboration, transparency, and shared responsibility. The GAO report Effective Practices and Federal Challenges in Applying Agile Methods recommends four organizational commitment and collaboration practices for Agile implementations:
- Ensure all components involved in projects are committed to the organization’s Agile approach
- Identify an Agile champion within senior management
- Ensure all teams include coaches or staff with Agile experience
- Empower small, cross-functional teams
Implementing these practices will help facilitate the cultural changes necessary to make Agile effective. As noted in the GAO report, several challenges relate to significant differences in how projects are managed in an Agile environment. Previous government attempts with Agile have produced mixed to poor results because the government tried to implement portions of Agile without changing some of the underlying development environments, tools, processes, and culture, which remained oriented toward traditional development strategies. Rather than simply follow a recipe of Agile methods and steps, programs should try to adopt the Agile philosophy and mindset to instill program agility. Establishing an organizational change discipline and clear vision can help to communicate the organizations strategy of adopting the Agile philosophy. The functional communities supporting acquisition today often operate in silos with only weak ties to the program office. Agile practices require a complementary business environment to provide the structure, discipline, and support for Agile development practices. For Agile to succeed, the environment must facilitate close collaboration across multiple disciplines to support rapid development cycles. A successful Agile framework depends on active support from multiple stakeholder communities, including users, developers, systems engineers, and testing and certification staff, as well as DoD leadership and oversight. Program managers must engage these key stakeholders to garner their endorsement and feedback and to build an Agile culture that can be sustained throughout the lifecycle of DoD IT programs.
See the Agile Culture Panel (video) at a DAU Hot Topic Forum featuring experts from OSD, DAU, SEI, CACI, and RCAS.
Agile Teams
Agile development requires that both the contractor development team and the government program office adopt a new set of roles and responsibilities. The figure below shows a potential Agile team construct. At the heart of an Agile development effort is the release team responsible for execution. The release team includes a core team composed of the project manager, product owner, tester, and systems engineer, and a development team led by a scrum master (scrum master and Product Owner are roles specific to the Scrum methodology, team roles may vary if using other Agile methods). The broader extended team includes primary stakeholders and representatives of functional support activities, to include the acquisition leadership, contracting, test, certification and accreditation (C&A), the user community, external systems, and organizations contributing financial support.
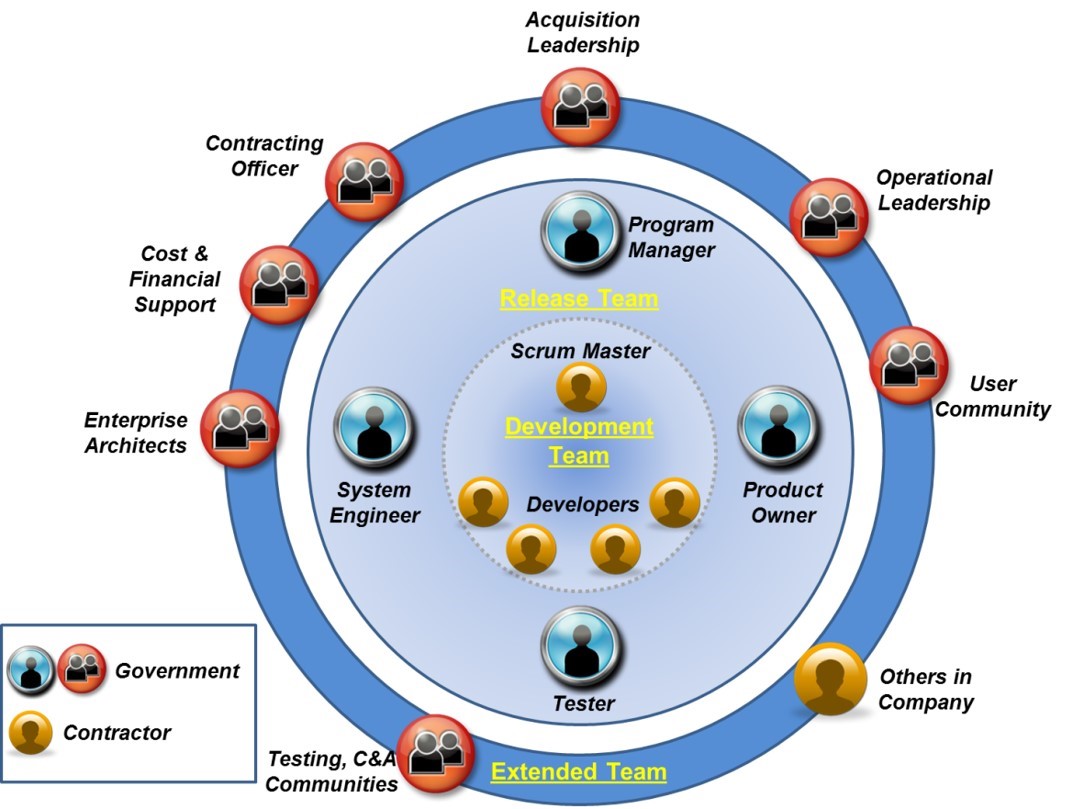 Potential Agile Team Construct
Potential Agile Team Construct
While the roles may vary based on the Agile methodologies and level of integration, four roles recur in almost all Agile activities.
- The Product Owner is the authoritative user community representative who manages the backlog(s) and requirements prioritization, communicates operational concepts to the development team, and provides continual feedback to the development team on their products. See analyze requirements for additional details on this role. The Product Owner is frequently a government employee from the user organization that owns the requirements, but some programs have a contractor fill this role and then work with government users.
- The scrum master facilitates the processes, enforces the team’s rules, removes barriers, and keeps the team focused on tasks. The scrum master is usually a contractor who is a member of the development team.
- The release team is composed of <10 government and contractor members who work closely together on the release.
- The development team is typically composed of contractor staff: software developers, including software and security engineers, data specialists, testers, quality assurance, and configuration managers.
Ideally these participants are co-located in the same physical space. When co-location is not achievable, they should meet regularly via phone or in person, and maximize use of collaboration tools.
While Agile practices depend upon highly skilled and disciplined team members, a cross-functional team of mentors and experts working alongside junior-level team members can also succeed. Program offices realize the best results when the team has at least one staff member with Agile or related expertise who provides on-the-job training to the other staff and is committed to leading teams through successful adoption of Agile practices.
Members of effective program teams understand their roles and responsibilities within an Agile program and have confidence in their ability to perform them. The applicable Agile guidelines for obtaining the necessary talent include:
- Recruit personnel with Agile, Lean, and related expertise to join the program team. Program managers should look across programs in the next higher level organization (e.g., PEO level) and should advocate sharing of those critical skill assets.
- Bring in experts in Agile, Lean, and related methodologies to serve as Agile coaches and to conduct on-the-job-training for the program office staff. These experts can make invaluable contributions by guiding the program office to identify and improve roles, processes, and techniques, while addressing any adoption issues. Agile coaches help bring all program participants together under a common set of practices and guidelines.
Management of Agile development requires a shift from the traditional model of directing projects from the top down to one of trusting and empowering teams to make decisions and to collaborate on solutions. Programs must operate in a trusting and cooperative manner across the government, contractors, and development teams. This may require the government to refine or redefine existing roles and consider new roles specific to Agile. The table below identifies recommended roles and responsibilities for members of an Agile team.
Recommended Roles and Responsibilities
| Role | Responsibilities |
| Program Manager | Manages the requirements, funding, and acquisition processes while also overseeing the planning of each release and high-level program increment. |
| Product Owner | Manages the requirements, tradeoffs, and collaboration between the acquisition and user communities. |
| Scrum Master | Facilitates the developers as they execute their processes, shielding the team from distractions. Enforces the development team rules and keeps the team focused on tasks. Often manages the sprint backlog. |
| Developers | Develops the software, to include software developers, database administrators and architects, testers, and other technical experts. |
| End Users | Convey operational concepts and requirements/needs, participate in continuous testing activities, and provide feedback on developed capabilities. |
| Enterprise Architect | Creates architectures and designs in an iterative manner to ensure that designs evolve in a controlled way over the course of releases. |
| Independent Tester(s) | Validates the capabilities produced against the end users’ top-priority needs, the design specifications, and standards. |
| Systems Engineer | Manages releases, overseeing system implementations, O&M, and transition, and integrates all the engineering sub disciplines and specialty groups into a team effort to create a structured development process. |
| Contracting Officer | Manages the solicitation, award, and execution of Agile development contracts, and facilitates communication between government and contractor staff. |
| Contracting Officer’s Representative (COR) | Acts as a representative to the Contracting Officer. The COR does not have authority to make changes to the contract or authorize new work; however, the COR is critical in ensuring the vendor executes the technical work in compliance with the contract. |
| Cost Estimator | Tracks and manages the overall program budgets; provides low-fidelity cost estimates at the program-level for high-level increments, followed by detailed cost estimates prior to the development of each release. |
Key Questions to Validate Agile Teams/Roles:
- Are the major stakeholder roles and responsibilities clearly defined?
- Is there a clear owner of the requirements backlog?
- Is there a clear government integrator (e.g., program manager and/or systems engineer) who coordinates and integrates programmatics (e.g., schedules, metrics) and deliverables (e.g., code)?
- Is there a clear owner of the program (or broader enterprise) architecture?
- Is there a clear, early commitment from user representatives and the broader user base?
- Are users co-located with, or within close proximity to the program office and/or contractor?
- How frequently do users meet (face-to-face, phone, VTC) with the PMO and developers?
- Is the Product Owner empowered to speak on behalf of the user community?
- Does the effort actively engage a collaborative, cross-functional community of stakeholders?
- Is the team size small enough to effectively adopt Agile principles?
- Are the number of teams manageable per the size, risk, complexity, and integration required?
- Is there a system-of-systems, scrum-of-scrums, or related cross-team integration role?
- Have approval authorities been delegated to a low enough level to enable rapid decisions?
- Do teams comprise both government representatives and developers?
- Do the team members have sufficient Agile experience, training, and/or coaches?
- Do external stakeholders understand and support their roles in an Agile environment?
See also:
- Roles on Disciplined Agile Delivery Teams by Scott Ambler
- Roles on Agile Teams, Ambysoft
- Agile Retrospectives: Making Good Teams Great, Esther Derby, Diana Larsen
- 42 Tasks for a Scrum Master, Agile Trail
- Scaling Agile
Multiple Agile Teams
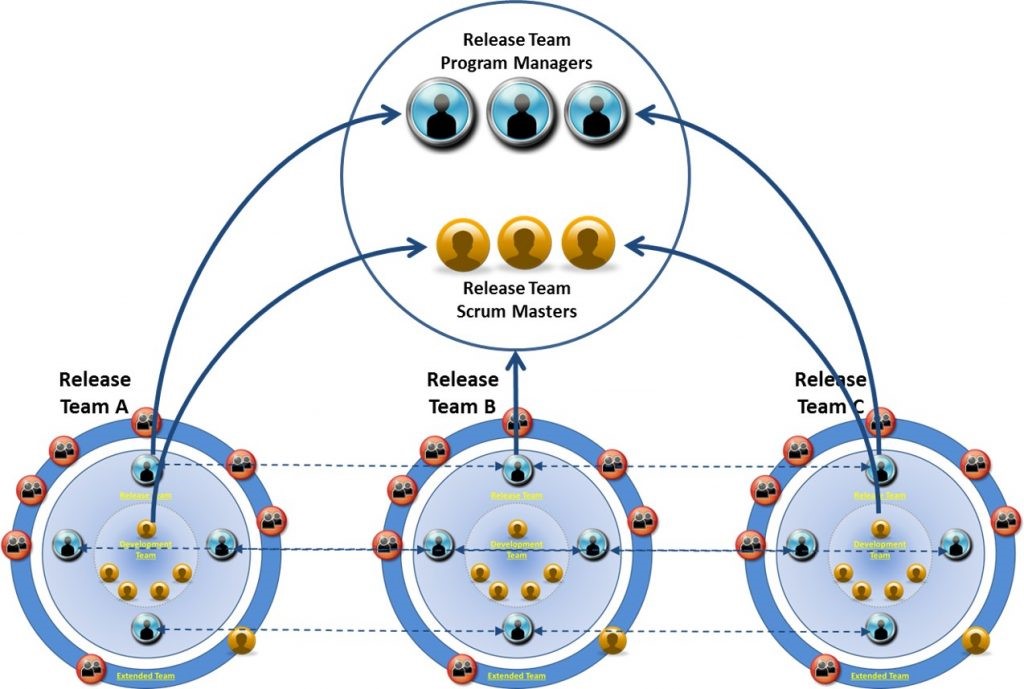
Agile development often involves multiple teams working on a single program. For example, one team could be assigned a release to develop in parallel with one or more other teams developing other releases. This requires active coordination of efforts across the teams to ensure they are developing towards a common solution. Adding development teams enables faster delivery of more software, yet comes with increased risk to coordinate, integrate, and manage these developments and teams. There are various approaches to structure a multi-team environment.
The next figure shows multiple development teams (all contractors) each working on its own release. The scrum masters of each team would meet regularly (e.g., weekly) with government personnel. This approach may limit the government’s, particularly the Product Owner’s, involvement with the development teams, but enables the development team to focus on its tasks with minimal interruption.
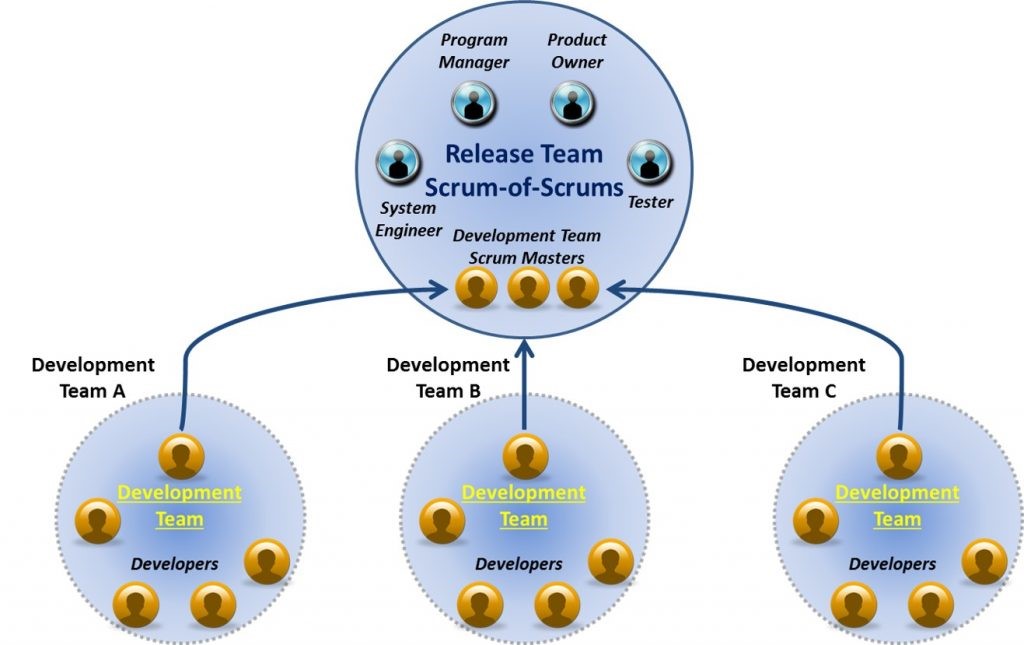 Multiple Development Teams Example
Multiple Development Teams Example
The figure below highlights multiple release teams of government and contractor personnel, with government and contractor representatives from each team regularly collaborating via a scrum-of-scrums. These representatives can be the PM and scrum master. A single Product Owner could support all the release teams and scrum-of-scrums efforts. Team members can regularly collaborate with those in similar roles on other teams on progress, designs, dependencies, issues, and resources. This approach focuses on an integrated government-contractor release team, but could be more resource intensive.
See also:
GAO 10 Best Practices and 14 Challenges for Agile Adoption
GAO’s Report on Effective Practices and Federal Challenges in Applying Agile Methods outlines:
10 Best Practices for Agile Adoption
- Start with Agile guidance and an Agile adoption strategy
- Enhance migration to Agile concepts using Agile terms, such as user stories (used to convey requirements), and Agile examples, such as demonstrating how to write a user story
- Continuously improve Agile adoption at both the project level and organization level
- Identify, address impediments at the organization and project levels
- Obtain stakeholder/customer feedback frequently
- Empower small, cross-functional teams
- Include requirements related to security and progress monitoring in your queue of unfinished work (the backlog)
- Gain trust by demonstrating value at the end of each iteration
- Track progress using tools and metrics
- Track progress daily and visibly
14 Challenges to Agile Adoption
- Teams had difficulty collaborating closely
- Procurement practices may not support Agile projects
- Teams had difficulty transitioning to self-directed work
- Customers did not trust iterative solutions
- Staff had difficulty committing to more timely and frequent input
- Teams had difficulty managing iterative requirements
- Agencies had trouble committing staff
- Compliance reviews difficult to execute within an iteration timeframe
- Timely adoption of new tools was difficult
- Federal reporting practices do not align with Agile
- Technical environments were difficult to establish and maintain
- Traditional artifact reviews do not align with Agile
- Agile guidance was not clear
- Traditional status tracking does not align with Agile
Source: GAO Report 12-681 Effective Practices and Federal Challenges in Applying Agile Methods
FY18 NDAA Section 873 Agile Pilots
SEC. 873. PILOT PROGRAM TO USE AGILE OR ITERATIVE DEVELOPMENT METHODS TO TAILOR MAJOR SOFTWARE-INTENSIVE WARFIGHTING SYSTEMS AND DEFENSE BUSINESS SYSTEMS.
(a) Pilot Program.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Not later than 30 days after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Secretary of Defense, in consultation with the Secretaries of the military departments and the chiefs of the armed forces, shall establish a pilot program to tailor and simplify software development requirements and methods for major software-intensive warfighting systems and defense business systems.
(2) IMPLEMENTATION PLAN FOR PILOT PROGRAM.—Not later than 120 days after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Secretary of Defense, in consultation with the Secretaries of the military departments and the chiefs of the armed forces, shall develop a plan for implementing the pilot program required under this subsection, including guidance for implementing the program and for selecting systems for participation in the program.
(3) SELECTION OF SYSTEMS FOR PILOT PROGRAM.—
(A) The implementation plan shall require that systems be selected as follows:
(i) For major software-intensive warfighting systems, one system per armed force and one defense-wide system, including at least one major defense acquisition program or major automated information system.
(ii) For defense business systems, not fewer than two systems and not greater than eight systems.
(B) In selecting systems for participation, the Secretary shall prioritize systems as follows:
(i) For major software-intensive warfighting systems, systems that—
(I) have identified software development as a high risk;
(II) have experienced cost growth and schedule delay; and
(III) did not deliver any operational capability within the prior calendar year.
(ii) For defense business systems, systems that—
(I) have experienced cost growth and schedule delay;
(II) did not deliver any operational capability within the prior calendar year; and
(III) are underperforming other systems within a defense business system portfolio with similar user requirements.
(b) Realignment Plans.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Not later than 60 days after selecting a system for the pilot program under subsection (a)(3), the Secretary shall develop a plan for realigning the system by breaking down the system into smaller increments using agile or iterative development methods. The realignment plan shall include a revised cost estimate that is lower than the cost estimate for the system that was current as of the date of the enactment of this Act.
(2) REALIGNMENT EXECUTION.—Each increment for a realigned system shall—
(A) be designed to deliver a meaningfully useful capability within the first 180 days following realignment;
(B) be designed to deliver subsequent meaningfully useful capabilities in time periods of less than 180 days;
(C) incorporate multidisciplinary teams focused on software production that prioritize user needs and control of total cost of ownership;
(D) be staffed with highly qualified technically trained staff and personnel with management and business process expertise in leadership positions to support requirements modification, acquisition strategy, and program decisionmaking;
(E) ensure that the acquisition strategy for the realigned system is broad enough to allow for proposals of a service, system, modified business practice, configuration of personnel, or combination thereof for implementing the strategy;
(F) include periodic engagement with the user community, as well as representation by the user community in program management and software production activity;
(G) ensure that the acquisition strategy for the realigned system favors outcomes-based requirements definition and capability as a service, including the establishment of technical evaluation criteria as outcomes to be used to negotiate service-level agreements with vendors; and
(H) consider options for termination of the relationship with any vendor unable or unwilling to offer terms that meet the requirements of this section.
(c) Removal Of Systems.—The Secretary may remove a system selected for the pilot program under subsection (a)(3) only after the Secretary submits to the Committees on Armed Services of the Senate and House of Representatives a written determination that indicates that the selected system has been unsuccessful in reducing cost or schedule growth, or is not meeting the overall needs of the pilot program.
(d) Education And Training In Agile Or Iterative Development Methods.—
(1) TRAINING REQUIREMENT.—The Secretary shall ensure that any personnel from the relevant organizations in each of the military departments and Defense Agencies participating in the pilot program, including organizations responsible for engineering, budgeting, contracting, test and evaluation, requirements validation, and certification and accreditation, receive targeted training in agile or iterative development methods, including the interim course required by section 891 of this Act.
(2) SUPPORT.—In carrying out the pilot program under subsection (a), the Secretary shall ensure that personnel participating in the program provide feedback to inform the development of education and training curricula as required by section 891.
(e) Sunset.—The pilot program required under subsection (a) shall terminate on September 30, 2023. Any system selected under subsection (a)(3) for the pilot program shall continue after that date through the execution of its realignment plan.
(f) Agile Or Iterative Development Defined.—In this section, the term “agile or iterative development”, with respect to software—
(1) means acquisition pursuant to a method for delivering multiple, rapid, incremental capabilities to the user for operational use, evaluation, and feedback not exclusively linked to any single, proprietary method or process; and
(2) involves—
(A) the incremental development and fielding of capabilities, commonly called “spirals”, “spins”, or “sprints”, which can be measured in a few weeks or months; and
(B) continuous participation and collaboration by users, testers, and requirements authorities.
FY18 NDAA Section 874 Agile Pilots
(a) In General.—Not later than 30 days after the date of the enactment of this Act, the Secretary of Defense shall identify no fewer than four and up to eight software development activities within the Department of Defense or military departments to be developed in a pilot program using agile acquisition methods.
(b) Streamlined Processes.—Software development activities identified under subsection (a) shall be selected for the pilot program and developed without incorporation of the following contract or transaction requirements:
(1) Earned value management (EVM) or EVM-like reporting.
(2) Development of integrated master schedule.
(3) Development of integrated master plan.
(4) Development of technical requirement document.
(5) Development of systems requirement documents.
(6) Use of information technology infrastructure library agreements.
(7) Use of software development life cycle (methodology).
(c) Roles And Responsibilities.—
(1) IN GENERAL.—Selected activities shall include the following roles and responsibilities:
(A) A program manager that is authorized to make all programmatic decisions within the overarching activity objectives, including resources, funding, personnel, and contract or transaction termination recommendations.
(B) A product owner that reports directly to the program manager and is responsible for the overall design of the product, prioritization of roadmap elements and interpretation of their acceptance criteria, and prioritization of the list of all features desired in the product.
(C) An engineering lead that reports directly to the program manager and is responsible for the implementation and operation of the software.
(D) A design lead that reports directly to the program manager and is responsible for identifying, communicating, and visualizing user needs through a human-centered design process.
(2) QUALIFICATIONS.—The Secretary shall establish qualifications for personnel filling the positions described in paragraph (1) prior to their selection. The qualifications may not include a positive education requirement and must be based on technical expertise or experience in delivery of software products, including agile concepts.
(3) COORDINATION PLAN FOR TESTING AND CERTIFICATION ORGANIZATIONS.—The program manager shall ensure the availability of resources for test and certification organizations support of iterative development processes.
(d) Plan.—The Secretary of Defense shall develop a plan for each selected activity under the pilot program. The plan shall include the following elements:
(1) Definition of a product vision, identifying a succinct, clearly defined need the software will address.
(2) Definition of a product road map, outlining a noncontractual plan that identifies short-term and long-term product goals and specific technology solutions to help meet those goals and adjusts to mission and user needs at the product owner’s discretion.
(3) The use of a broad agency announcement, other transaction authority, or other rapid merit-based solicitation procedure.
(4) Identification of, and continuous engagement with, end users.
(5) Frequent and iterative end user validation of features and usability consistent with the principles outlined in the Digital Services Playbook of the U.S. Digital Service.
(6) Use of commercial best practices for advanced computing systems, including, where applicable—
(A) Automated testing, integration, and deployment;
(B) compliance with applicable commercial accessibility standards;
(C) capability to support modern versions of multiple, common web browsers;
(D) capability to be viewable across commonly used end user devices, including mobile devices; and
(E) built-in application monitoring.
(e) Program Schedule.—The Secretary shall ensure that each selected activity includes—
(1) award processes that take no longer than three months after a requirement is identified;
(2) planned frequent and iterative end user validation of implemented features and their usability;
(3) delivery of a functional prototype or minimally viable product in three months or less from award; and
(4) follow-on delivery of iterative development cycles no longer than four weeks apart, including security testing and configuration management as applicable.
(f) Oversight Metrics.—The Secretary shall ensure that the selected activities—
(1) use a modern tracking tool to execute requirements backlog tracking; and
(2) use agile development metrics that, at a minimum, track—
(A) pace of work accomplishment;
(B) completeness of scope of testing activities (such as code coverage, fault tolerance, and boundary testing);
(C) product quality attributes (such as major and minor defects and measures of key performance attributes and quality attributes);
(D) delivery progress relative to the current product roadmap; and
(E) goals for each iteration.
(g) Restrictions.—
(1) USE OF FUNDS.—No funds made available for the selected activities may be expended on estimation or evaluation using source lines of code methodologies.
(2) CONTRACT TYPES.—The Secretary of Defense may not use lowest price technically acceptable contracting methods or cost plus contracts to carry out selected activities under this section, and shall encourage the use of existing streamlined and flexible contracting arrangements.
(h) Reports.—
(1) SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT ACTIVITY COMMENCEMENT.—
(A) IN GENERAL.—Not later than 30 days before the commencement of a software development activity under the pilot program under subsection (a), the Secretary shall submit to the congressional defense committees a report on the activity (in this subsection referred to as a “pilot activity”).
(B) ELEMENTS.—The report on a pilot activity under this paragraph shall set forth a description of the pilot activity, including the following information:
(i) The purpose of the pilot activity.
(ii) The duration of the pilot activity.
(iii) The efficiencies and benefits anticipated to accrue to the Government under the pilot program.
(2) SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT ACTIVITY COMPLETION.—
(A) IN GENERAL.—Not later than 60 days after the completion of a pilot activity, the Secretary shall submit to the congressional defense committees a report on the pilot activity.
(B) ELEMENTS.—The report on a pilot activity under this paragraph shall include the following elements:
(i) A description of results of the pilot activity.
(ii) Such recommendations for legislative or administrative action as the Secretary considers appropriate in light of the pilot activity.
(i) Definitions.—In this section:
(1) AGILE ACQUISITION.—The term “agile acquisition” means acquisition using agile or iterative development.
(2) AGILE OR ITERATIVE DEVELOPMENT.—The term “agile or iterative development”, with respect to software—
(A) means acquisition pursuant to a method for delivering multiple, rapid, incremental capabilities to the user for operational use, evaluation, and feedback not exclusively linked to any single, proprietary method or process; and
(B) involves—
(i) the incremental development and fielding of capabilities, commonly called “spirals”, “spins”, or “sprints”, which can be measured in a few weeks or months; and
(ii) continuous participation and collaboration by users, testers, and requirements authorities.
References:
- GAO Effective Practices and Federal Challenges in Applying Agile Methods
- TechFAR Handbook for Procuring Digital Services using Agile Processes
- Agile Acquisition 101 Video, Matt Kennedy
- DISA IT Acquisition Guide – 9 Tailored Acquisition Models
- Why developers consider Agile development to be nonsense, Kevin W., Jan 2019
- Agile Is Ruining Your Product, Matt LeMary, Jan 2019
- FAA Agile Acquisition Guide
- CMS Expeditionary Lifecycle (XLC) Process
- Critical Decision Factors for Agile in Federal IT Projects, MITRE, Nov 2015
- Disciplined Agile Delivery, Scott Ambler, Mark Lines
- Scrum: a Breathtakingly Brief and Agile Introduction, by
- 10th Annual State of Agile Report, VersionOne
- Considerations for Using Agile in DoD Acquisition, SEI, Dec 2016
- Embracing Agile, HBR by Darrell Rigby, Jeff Sutherland, Hirotaka Takeuchi, May 2016
- Enabling Acquisition Success for Agile Development, Frank McNally, Feb 2014
- Toward a More Agile Government, Ben Balter
- Planning for Success: Agile Software Development in Federal Agencies, ACT-IAC, Aug 2013
- The Challenges of Being Agile in DoD, William Broadus, Jan 2013
- Agile Methods: Selected DoD Management and Acquisition Concerns, SEI, Oct 2011
- Agile Glossary, Agile Alliance
- Scrum Training Videos, ScrumStudy
- Agile Acquisition 101, Federal Acquisition Institute
- Agile Government Handbook, AGL
- Agile Project Management for Government, Brian Wernham
- The new government leader: Mobilizing agile public leadership, Katherine Ryan & Abed Ali
- 4 Roadblocks to Agile Development and How to Overcome Them, David Raths